걸음마부터 달리기
[24/10/9] 코테 본문
백준 11660

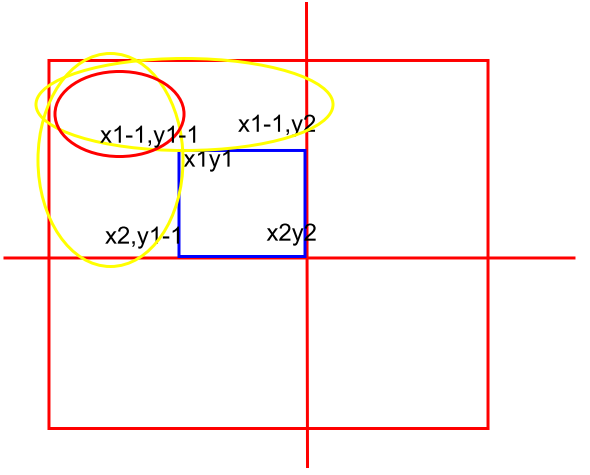
일단 구간합 D 배열을 만든다. 이때 D 배열은 (0,0) 부터 (x2,y2) 까지 모두 더한 값을 D[x2,y2]로 정의한다.
근데 우리가 구하고자하는 값은 (x1,y1)~(x2,y2) 의 사각형 부분의 합이니까
D[x2][y2]-D[x2][y1-1]-D[x1-1][y2]+D[x1-1][y1-1] 의 작전으로 짜면 된다.
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
// N쪽에선 O(n^2) 가능하고 M쪽에선 O(N)
// 구간합 배열 만들땐 이중 for문으로 만들고 M에서 출력
// The main method must be in a class named "Main".
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int A[][] = new int[N+1][N+1];
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++){
st=new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int j=1; j<=M; j++){
A[i][j]=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
int D[][] = new int[N+1][N+1];
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++){
for(int j=1; j<=N; j++){
D[i][j]=D[i-1][j]+D[i][j-1]-D[i-1][j-1]+A[i][j];
}
}
for(int i=0; i<M; i++){
st=new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int x1 = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y1= Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int x2= Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y2= Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int result = D[x2][y2]-D[x2][y1-1]-D[x1-1][y2]+D[x1-1][y1-1];
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}
//(2,2) >> 6 == 2*4 - (4-2)
// (3,3) >> 11
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
백준 1940번
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
// 1 2 3 4 5 7
// 2초에 N이 15000이라 O(N^2) (15000)^2 < 1억*2 니까 브루트포스로 풀어도 되긴함
// 투포인터면 O(2N) 으로 끝날듯
// The main method must be in a class named "Main".
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int[] arr = new int[N+1];
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++){
arr[i]=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
Arrays.sort(arr);
//N개면 0~N-1까지...
//sum보다 크면 end_index 줄이고
//sum보다 작으면 start_index 키우고
//같으면 start_index를 하나 키우고
int count =0;
int start_index=1;
int end_index=N;
int sum= arr[start_index]+arr[end_index];
while(start_index!=end_index){
if(sum>M){
end_index--;
sum=arr[start_index]+arr[end_index];
}
else if(sum<M){
start_index++;
sum=arr[start_index]+arr[end_index];
}
else{
count++;
start_index++;
sum=arr[start_index]+arr[end_index];
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
시간제한이 2초로 널널한 편이라 브루트포스로 이중포문 다 돌면서 해도 통과는 했을거지만 배울게 없다.
투포인터로 써보자.
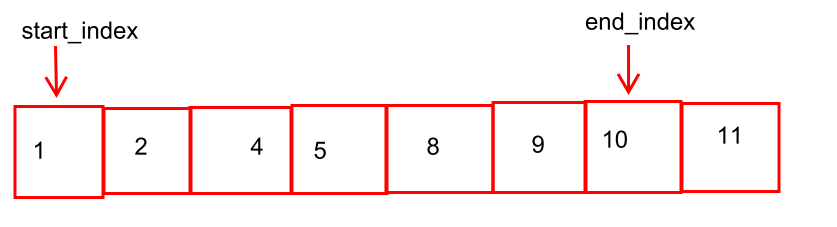
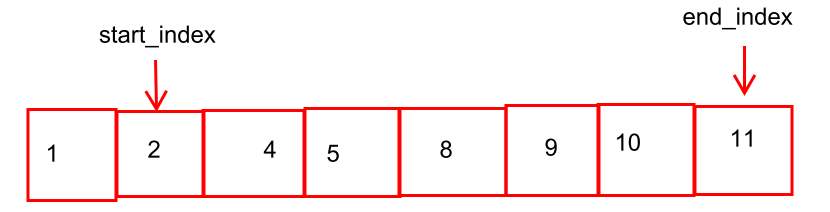
기존의 투포인터 예시에서는 정렬되어 있는 상태에서 크냐 작냐를 가지고 작으면 sum을 키워주기 위해 end_index++,
sum이 기준값보다 크면 sum을 작게 하기 위해서 start_index++; 를 해줬다,
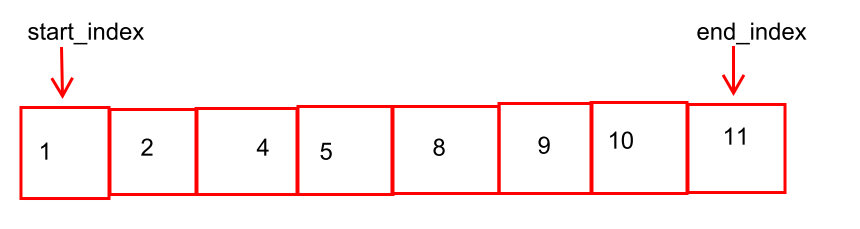
근데 얘는 2가지만 더하는 예제이고 배열 원소가 정렬되어 있지 않으면 start_index와 end_index를 움직일 수가 없어 일단 정렬시켰다.
그런데 기존 예시처럼 start_index++혹은 end_index++를 하면 무조건 커지는 방향으로 진행되기에 sum이 작아지게 고려할려고 end_index를 오른쪽 끝으로 잡았다.
--------------------------
백준 1253
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
// 1 2 3 4 5 7
// 2초에 N이 15000이라 O(N^2) (15000)^2 < 1억*2 니까 브루트포스로 풀어도 되긴함
// 투포인터면 O(2N) 으로 끝날듯
// The main method must be in a class named "Main".
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//for문으로 앞에서부터 하나씩 잡아서
//start_index =1 ; end_index=i-1
// sum이 작으면 start_index++
//sum이 크면 end_index--
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
st=new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
long[] arr = new long[N];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
arr[i]=Long.parseLong(st.nextToken());
}
Arrays.sort(arr);
int count=0;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
int start_index=0;
int end_index=N-1;
long M = arr[i];
long sum=arr[start_index]+arr[end_index];
while(start_index!=end_index){ //end_index==i ,
if(sum==M){
if(end_index!=i && start_index != i){
count++;
break;
}
else if(start_index==i){
start_index++;
sum=arr[start_index]+arr[end_index];
}
else if(end_index==i){
end_index--;
sum=arr[start_index]+arr[end_index];
}
}
else if(sum>M){
end_index--;
sum=arr[start_index]+arr[end_index];
}
else { //sum<M
start_index++;
sum=arr[start_index]+arr[end_index];
}
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
풀이는 위의 문제와 같은데 반례를 좀 조심해야 되는 문제다.
자꾸 테케 한두개에서 삐끗났었는데 이유는 배열 원소 중 0이 있을 경우 문제가 생긴다.
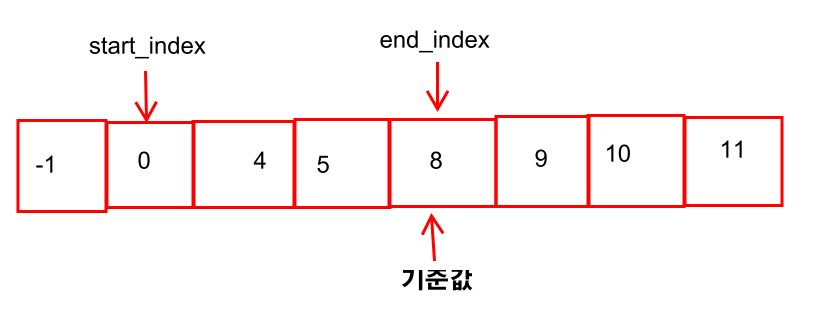
바로 이런 경우이다. 0+8==8(기준값) 으로 맞는 경우라고 생각하면 안된다. 기준값에 해당하는 인덱스 제외 서로 다른 2개의 배열 원소값을 더해야해서 이런 경우 (end_index==기준 index , start_index==기준 index) 에 대하여 if로 예외처리만 해주면 된다.